Related Research Articles

2C-I is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and described in his 1991 book PiHKAL. The drug has been used recreationally as psychedelic and other reported effects and was sometimes confused with the more potent chemical cousin 25I-NBOMe, nicknamed "Smiles," in the media.
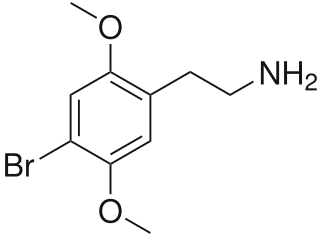
2C-B (4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a psychedelic drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1974. In Shulgin's book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 12–24 mg. As a recreational drug, 2C-B is sold as a white powder sometimes pressed in tablets or gel caps. It is also referred to by a number of street names. The drug is usually taken orally, but can also be insufflated or vaporized. While being primarily a psychedelic it is also a mild entactogen.

2C-C is a psychedelic drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, sometimes used as an entheogen. In his book PiHKAL , Shulgin lists the dosage range as 20–40 mg. 2C-C is usually taken orally, but may also be insufflated. 2C-C is schedule I of section 202(c) of the Controlled Substances Act in the United States, signed into law as of July, 2012 under the Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act.
Gray death is a slang term which refers to a potent mixture of synthetic opioids, for example benzimidazole opioids or fentanyl analogues, often sold on the street as a proven substance. However, other substances such as stimulants have also been laced with opioids that resulted in deaths.

2C-G is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. First synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, it is sometimes used as an entheogen. It has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to 2C-D and Ganesha. Like many of the phenethylamines in PiHKAL, 2C-G and its homologs have only been taken by Shulgin and a small test group, making it difficult to ensure completeness when describing effects.
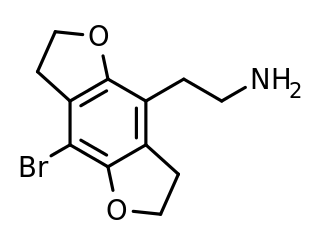
2C-B-FLY is a psychedelic phenethylamine and designer drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized in 1996 by Aaron P. Monte.
Dimethoxyamphetamine (DMA) is a series of six lesser-known psychedelic drugs similar in structure to the three isomers of methoxyamphetamine and six isomers of trimethoxyamphetamine. The isomers are 2,3-DMA, 2,4-DMA, 2,5-DMA, 2,6-DMA, 3,4-DMA, and 3,5-DMA. Three of the isomers were characterized by Alexander Shulgin in his book PiHKAL. Little is known about their dangers or toxicity.

25I-NBOH is a derivative of the phenethylamine-derived hallucinogen 2C-I that was discovered in 2006 by a team at Purdue University.

2CBCB-NBOMe (NBOMe-TCB-2) is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine series of hallucinogens, which was discovered in 2007 at Purdue University as part of the ongoing research program of the team led by David Nichols focusing on the mapping of the specific amino acid residues responsible for ligand binding to the 5HT2A receptor. 2CBCB-NBOMe acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, with a Ki of 0.27 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor, a similar potency to other agonists such as TCB-2, NBOMe-2C-I and Bromo-DragonFLY.
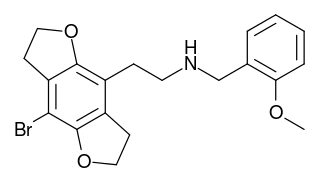
2CBFly-NBOMe is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, and related to benzodifurans like 2C-B-FLY and N-benzylphenethylamines like 25I-NBOMe. It was discovered in 2002, and further researched by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin, and subsequently investigated in more detail by a team at Purdue University led by David E. Nichols. It acts as a potent partial agonist for the 5HT2A serotonin receptor subtype.

25I-NBMD is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-I, discovered in 2006 by a team at Purdue University led by David Nichols. It acts as a potent partial agonist for the 5HT2A receptor with a Ki of 0.049 nM at the human 5HT2A receptor. The corresponding 4-bromo analogue 25B-NBMD has been used for molecular dynamics studies on the shape of the 5-HT2A receptor.

25B-NBOMe is a derivative of the phenethylamine psychedelic 2C-B, discovered in 2004 by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin. It acts as a potent full agonist for the 5HT2A receptor. Anecdotal reports from users suggest 25B-NBOMe to be an active hallucinogen at a dose of as little as 250–500 µg, making it a similar potency to other phenethylamine derived hallucinogens such as Bromo-DragonFLY. Duration of effects lasts about 12–16 hours, although the parent compound is rapidly cleared from the blood when used in the radiolabeled form in tracer doses. Recently, Custodio et al (2019) evaluated the potential involvement of dysregulated dopaminergic system, neuroadaptation, and brain wave changes which may contribute to the rewarding and reinforcing properties of 25B-NBOMe in rodents.

2CB-Ind is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, discovered in 1974 by Alexander Shulgin. It acts as a moderately potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, but unlike the corresponding benzocyclobutene derivative TCB-2 which is considerably more potent than the parent compound 2C-B, 2CB-Ind is several times weaker, with racemic 2CB-Ind having a Ki of 47nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor, only slightly more potent than the mescaline analogue (R)-jimscaline.
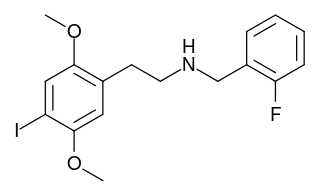
25I-NBF is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-I, which acts as a highly potent partial agonist for the human 5-HT2A receptor, with bias towards the β-arrestin 2 coupled signalling pathway. It has been studied in its 11C radiolabelled form as a potential ligand for mapping the distribution of 5-HT2A receptors in the brain, using positron emission tomography (PET).
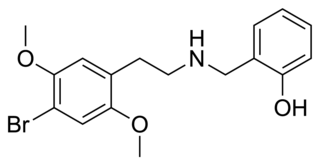
25B-NBOH is a derivative of the phenethylamine derived hallucinogen 2C-B which has been sold as a designer drug. It acts as a potent serotonin receptor agonist with similar affinity to the better-known compound 25B-NBOMe at 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors with pKis values of 8.3 and 9.4, respectively.
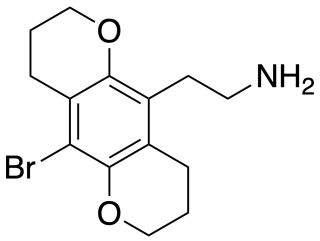
2C-B-BUTTERFLY is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, which was discovered in 1999 by Michael S. Whiteside and Aaron Monte. It is a ring-expanded homologue of the better known compound 2C-B-FLY, and has similar properties as an agonist for serotonin receptors, but with more selectivity for 5-HT2C over 5-HT2A.

25I-NB34MD (NB34MD-2C-I) is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-I, which acts as a potent partial agonist for the human 5-HT2A receptor, and presumably has similar properties to 2C-I. It has a binding affinity of 0.67nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor, making it several times weaker than its positional isomer 25I-NBMD and a similar potency to 25I-NBF.
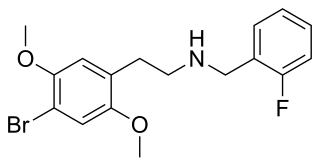
25B-NBF is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, which acts as a highly potent partial agonist for the human 5-HT2A receptor.

25C-NBF is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-C, which acts as a highly potent partial agonist for the human 5-HT2A receptor.
References
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-B)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-C)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-D)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-E)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-G)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-H)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-I)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-IP)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-N)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-P) fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-T)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-T-2)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-T-4)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-T-7)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ↑ "Explore N-(2C-TFM)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.