Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula CH3CH(OH)CO2H. It is white in solid state and it is extremely soluble in water. Solubility is so high that 1 part of lactic acid can dissolve 12 parts of water. While in liquid state (dissolved state) it is a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of carboxyl group adjacent to the hydroxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate.

Butyric acid (from Ancient Greek: βούτῡρον, meaning "butter"), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in animal fat and plant oils, bovine milk, breast milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). Butyric acid has a taste somewhat like butter and an unpleasant odor. Mammals with good scent detection abilities, such as dogs, can detect it at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can only detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million. In food manufacturing, it is used as a flavoring agent.

β-Hydroxybutyric acid, also known as 3-hydroxybutyric acid, is an organic compound and a beta hydroxy acid with the chemical formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CO2H; its conjugate base is β-hydroxybutyrate, also known as 3-hydroxybutyrate. β-Hydroxybutyric acid is a chiral compound with two enantiomers: D-β-hydroxybutyric acid and L-β-hydroxybutyric acid. Its oxidized and polymeric derivatives occur widely in nature. In humans, D-β-hydroxybutyric acid is one of two primary endogenous agonists of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2), a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR).

Picamilon is a drug formed by a synthetic combination of niacin and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It was developed in the Soviet Union in 1969 and further studied in both Russia and Japan as a prodrug of GABA.

Acipimox is a niacin derivative used as a lipid-lowering agent. It reduces triglyceride levels and increases HDL cholesterol. It may have less marked adverse effects than niacin, although it is unclear whether the recommended dose is as effective as standard doses of niacin.

G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER), also known as G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPER gene. GPER binds to and is activated by the female sex hormone estradiol and is responsible for some of the rapid effects that estradiol has on cells.

G protein-coupled receptor 35 also known as GPR35 is a G protein-coupled receptor which in humans is encoded by the GPR35 gene. Heightened expression of GPR35 is found in immune and gastrointestinal tissues, including the crypts of Lieberkühn.

G-protein coupled receptor 31 also known as 12-(S)-HETE receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR31 gene. The human gene is located on chromosome 6q27 and encodes a G-protein coupled receptor protein composed of 319 amino acids.

Free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFA1), also known as GPR40, is a class A G-protein coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the FFAR1 gene. It is strongly expressed in the cells of the pancreas and to a lesser extent in the brain. This membrane protein binds free fatty acids, acting as a nutrient sensor for regulating energy homeostasis.

Free fatty acid receptor 3 (FFA3) is a G-protein coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the FFAR3 gene.

Psychosine receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR65 gene. GPR65 is also referred to as TDAG8.

G protein-coupled receptor 55 also known as GPR55 is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the GPR55 gene.

Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1 (HCA1), formerly known as G protein-coupled receptor 81 (GPR81), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCAR1 gene. HCA1, like the other hydroxycarboxylic acid receptors HCA2 and HCA3, is a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The primary endogenous agonist of HCA1 is lactic acid (and its conjugate base, lactate).

Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2), also known as niacin receptor 1 (NIACR1) and GPR109A, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the HCAR2 gene. HCA2, like the other hydroxycarboxylic acid receptors HCA1 and HCA3, is a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The primary endogenous agonists of HCA2 are D-β-hydroxybutyric acid and butyric acid (and their conjugate bases, β-hydroxybutyrate and butyrate). HCA2 is also a high-affinity biomolecular target for niacin (aka nicotinic acid).

Relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 4, also known as RXFP4, is a human G-protein coupled receptor.

Oxoeicosanoid receptor 1 (OXER1) also known as G-protein coupled receptor 170 (GPR170) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OXER1 gene located on human chromosome 2p21; it is the principle receptor for the 5-Hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid family of carboxy fatty acid metabolites derived from arachidonic acid. The receptor has also been termed hGPCR48, HGPCR48, and R527 but OXER1 is now its preferred designation. OXER1 is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is structurally related to the hydroxy-carboxylic acid (HCA) family of G protein-coupled receptors whose three members are HCA1 (GPR81), HCA2, and HCA3 ; OXER1 has 30.3%, 30.7%, and 30.7% amino acid sequence identity with these GPCRs, respectively. It is also related to the recently defined receptor, GPR31, for the hydroxyl-carboxy fatty acid 12-HETE.

The γ-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) receptor (GHBR), originally identified as GPR172A, is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds the neurotransmitter and psychoactive drug γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). As solute carrier family 52 member 2 (SLC52A2), it is also a transporter for riboflavin.
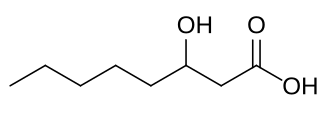
3-Hydroxyoctanoic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid that is naturally produced in humans, other animals, and plants.
The hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor (abbreviated HCA receptor and HCAR) family includes the following human proteins: