Related Research Articles

Korpokkur, also written Koro-pok-kuru, korobokkuru, korbokkur, or koropokkur, koro-pok-guru, are a race of small people in folklore of the Ainu people of the northern Japanese islands. The name is traditionally analysed as a tripartite compound of kor, pok, and kur ("person") and interpreted to mean "people below the leaves of the Fuki" in the Ainu language.
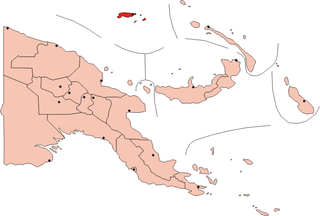
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island.

Manus Island is part of Manus Province in northern Papua New Guinea and is the largest of the Admiralty Islands. It is the fifth-largest island in Papua New Guinea, with an area of 2,100 km2 (810 sq mi), measuring around 100 km × 30 km. Manus Island is covered in rugged jungles which can be broadly described as lowland tropical rain forest. The highest point on Manus Island is Mt. Dremsel, 718 metres (2,356 ft) above sea level at the centre of the south coast. Manus Island is volcanic in origin and probably broke through the ocean's surface in the late Miocene, 8 to 10 million years ago. The substrate of the island is either directly volcanic or from uplifted coral limestone.
East Kameng district is one of districts of Arunachal Pradesh state in northeastern, India. It shares an international border with China in the north and district borders with West Kameng district to the west, Pakke-Kessang district to the south, Kurung Kumey district to the east, Papum Pare district to the southeast. Pakke-Kessang district was bifurcated from East Kameng district on 1 December 2018.
The Manus languages are a subgroup of about two dozen Oceanic languages located on Manus Island and nearby offshore islands in Manus Province of Papua New Guinea. The exact number of languages is difficult to determine because they form a dialect continuum. The name 'Manus' originally designated an ethnic group whose members spoke closely related languages and whose coastal dwellers tended to build their houses on stilts out over the sea.
Koro may refer to:

Koro is a volcanic island of Fiji that forms part of the Lomaiviti Archipelago. The Koro Sea is named after this volcanic island, which has a chain of basaltic cinder cones extending from north to south along its crest. With a land area of 103.2 square kilometers, it is the seventh largest island of Fiji. Its latitude is 17.18°; its longitude is 179.24°. Its population as of 2017 census was 2,937 spread across 14 villages on the island. A roll-on, roll-off ferry services Koro weekly from Suva, and also connects Koro to Vanua Levu to the North. Fiji Link provides one scheduled flight per week to Koro, usually on Friday from Nausori Airport.

The Koro Sea or Sea of Koro is a sea in the Pacific Ocean between Viti Levu island, Fiji to the west and the Lau Islands to the east, surrounded by the islands of the Fijian archipelago.

Gaua[gawa] is the largest and second most populous of the Banks Islands in Torba Province in northern Vanuatu. It covers 342 km².
Koch is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Koch people of Republic of India and Koch people in Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh.
The twenty Central Plateau languages are a residual branch of the Plateau family spoken in central Nigeria. Tyap has 130,000 speakers, and the closely related Jju has well over 300,000. Hyam has another 100,000. Cori is famous for being one of very few languages with six tone levels, though only three are needed for writing.
Koro is known as a Tibeto-Burman language belonging to the Sino-Tibetan language family, even though it has resemblances to Tani farther to the east. It has been argued that Koro is actually part of the Greater Siangic family, independent from but influenced by the Sino-Tibetan family. Koro is spoken by about 1,500 people in the Koro-Aka tribe who are found in the East Kameng District of Arunachal Pradesh in northeast India. Few speakers are under 20 years old. The majority of Koro speakers live in bilingual households in which one or more members speak Ako or another indigenous language rather than Koro. The Koro-Aka tribe lives among the Aka (Hruso) tribe. However, the Koro-Aka people speak a very distantly related language from the remaining Aka tribe who speak Hruso-Aka. Researchers hypothesize Koro may have originated from a group of people enslaved and brought to the area. Since there are so few people who speak Koro, it is considered an endangered language.
Koro is an Oceanic language spoken on Gaua island in Vanuatu. Its 280 speakers live in the village of Koro, on the south coast of Gaua.
Dorig(formerly called Wetamut) is an Oceanic language spoken on Gaua island in Vanuatu.
The Siangic languages are a small family of possibly Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Arunachal Pradesh, northeast India. The Siangic languages consist of Koro and Milang.
Loniu is an Austronesian language spoken along the southern coast of Los Negros Island in the Manus Province, immediately east of Manus Island in Manus Province, Papua New Guinea. Loniu is spoken in the villages of Loniu and Lolak, and there are estimated to be 450–500 native speakers, although some live in other Manus villages or on the mainland of PNG.
Greater Siangic is a language grouping that includes the Siangic languages, Digaro languages and Pre-Tani, the hypothetical substrate language branch of Tani before it became relexified by Sino-Tibetan. The Greater Siangic grouping was proposed by Roger Blench (2014), based on exclusively shared lexical items that had been noted by Modi (2013). Blench (2014) argues that Greater Siangic is an independent language family that has undergone areal influences from Sino-Tibetan languages, and is not a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family itself.
Koro–Olrat is a Glottolog classification that includes the following two languages of Gaua Island, Vanuatu:
The Torres–Banks languages form a linkage of Southern Oceanic languages spoken in the Torres Islands and Banks Islands of northern Vanuatu.
KXR or kxr may refer to:
References
- 1 2 Koro at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)