
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome.
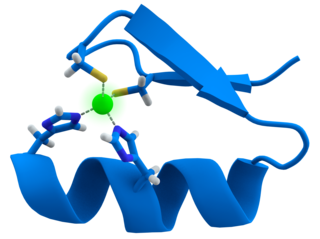
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) which stabilizes the fold. It was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from the African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) transcription factor IIIA. However, it has been found to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures in eukaryotic cells. Xenopus laevis TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein followed soon thereafter by the Krüppel factor in Drosophila. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins.

DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, because it exposes more functional groups that identify a base pair.

EGR-1 also known as ZNF268 or NGFI-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EGR1 gene.
This is a list of topics in molecular biology. See also index of biochemistry articles.

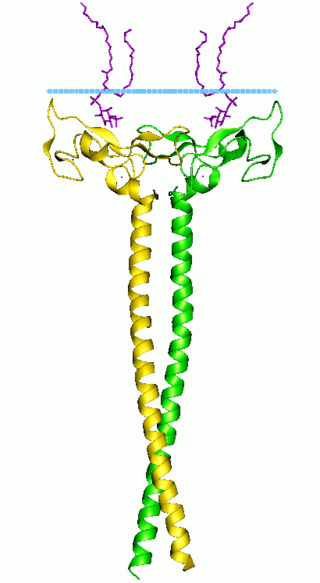
A leucine zipper is a common three-dimensional structural motif in proteins. They were first described by Landschulz and collaborators in 1988 when they found that an enhancer binding protein had a very characteristic 30-amino acid segment and the display of these amino acid sequences on an idealized alpha helix revealed a periodic repetition of leucine residues at every seventh position over a distance covering eight helical turns. The polypeptide segments containing these periodic arrays of leucine residues were proposed to exist in an alpha-helical conformation and the leucine side chains from one alpha helix interdigitate with those from the alpha helix of a second polypeptide, facilitating dimerization.
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure.
Chromosome 8 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 8 spans about 146 million base pairs and represents between 4.5 and 5.0% of the total DNA in cells.
C7 protein is an engineered zinc finger protein based on the murine ZFP, Zif268 and discovered by Wu et al. in 1994. It shares the same zinc finger 2 and zinc finger 3 of Zif268, but differs in the sequence of finger 1. It also shares the same DNA target, 5'-GCGTGGGCG-3'.
Therapeutic gene modulation refers to the practice of altering the expression of a gene at one of various stages, with a view to alleviate some form of ailment. It differs from gene therapy in that gene modulation seeks to alter the expression of an endogenous gene whereas gene therapy concerns the introduction of a gene whose product aids the recipient directly.

Artificial transcription factors (ATFs) are engineered individual or multi molecule transcription factors that either activate or repress gene transcription (biology).
In a zinc finger protein, certain sequences of amino acid residues are able to recognise and bind to an extended target-site of four or even five nucleotides When this occurs in a ZFP in which the three-nucleotide subsites are contiguous, one zinc finger interferes with the target-site of the zinc finger adjacent to it, a situation known as target-site overlap. For example, a zinc finger containing arginine at position -1 and aspartic acid at position 2 along its alpha-helix will recognise an extended sequence of four nucleotides of the sequence 5'-NNG(G/T)-3'. The hydrogen bond between Asp2 and the N4 of either a cytosine or adenine base paired to the guanine or thymine, respectively defines these two nucleotides at the 3' position, defining a sequence that overlaps into the subsite of any zinc finger that may be attached N-terminally.
In molecular biology the FYVE zinc finger domain is named after the four cysteine-rich proteins: Fab 1, YOTB, Vac 1, and EEA1, in which it has been found. FYVE domains bind phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, in a way dependent on its metal ion coordination and basic amino acids. The FYVE domain inserts into cell membranes in a pH-dependent manner. The FYVE domain has been connected to vacuolar protein sorting and endosome function.
Zinc finger protein chimera are chimeric proteins composed of a DNA-binding zinc finger protein domain and another domain through which the protein exerts its effect. The effector domain may be a transcriptional activator (A) or repressor (R), a methylation domain (M) or a nuclease (N).

Zinc finger protein 804A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF804A gene. The human gene maps to chromosome 2 q32.1 and consists of 4 exons that code for a protein of 1210 amino acids.

The BTB/POZ domain is a structural domain found in proteins across the domain Eukarya. Given its prevalence in eukaryotes and its absence in Archaea and bacteria, it likely arose after the origin of eukaryotes. While primarily a protein-protein interaction domain, some BTB domains have additional functionality in transcriptional regulation, cytoskeletal mobility, protein ubiquitination and degradation, and ion channel formation and operation. BTB domains have traditionally been classified by the other structural features present in the protein.

Genome editing, or genome engineering, or gene editing, is a type of genetic engineering in which DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the genome of a living organism. Unlike early genetic engineering techniques that randomly inserts genetic material into a host genome, genome editing targets the insertions to site-specific locations. The basic mechanism involved in genetic manipulations through programmable nucleases is the recognition of target genomic loci and binding of effector DNA-binding domain (DBD), double-strand breaks (DSBs) in target DNA by the restriction endonucleases, and the repair of DSBs through homology-directed recombination (HDR) or non-homologous end joining (NHEJ).
Zinc finger transcription factors or ZF-TFs, are transcription factors composed of a zinc finger-binding domain and any of a variety of transcription-factor effector-domains that exert their modulatory effect in the vicinity of any sequence to which the protein domain binds.
In molecular biology, a GC box, also known as a GSG box, is a distinct pattern of nucleotides found in the promoter region of some eukaryotic genes. The GC box is upstream of the TATA box, and approximately 110 bases upstream from the transcription initiation site. It has a consensus sequence GGGCGG which is position-dependent and orientation-independent. The GC elements are bound by transcription factors and have similar functions to enhancers. Some known GC box-binding proteins include Sp1, Krox/Egr, Wilms' tumor, MIGI, and CREA.
Since antiretroviral therapy requires a lifelong treatment regimen, research to find more permanent cures for HIV infection is currently underway. It is possible to synthesize zinc finger nucleotides with zinc finger components that selectively bind to specific portions of DNA. Conceptually, targeting and editing could focus on host cellular co-receptors for HIV or on proviral HIV DNA.









