Related Research Articles

The history of Madagascar is distinguished clearly by the early isolation of the landmass from the ancient supercontinent containing Africa and India, and by the island's late colonization by human settlers from the Sunda islands and from East Africa. These two factors facilitated the evolution and survival of thousands of endemic plant and animal species, some of which have gone extinct or are currently threatened with extinction. Trade in the Indian Ocean at the time of first colonization of Madagascar was dominated by Indonesian ships, probably of Borobudur ship and K'un-lun po types.
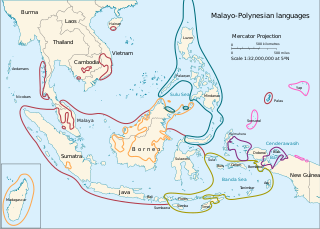
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages.

The Dayak or Dyak or Dayuh are one of the native groups of Borneo. It is a loose term for over 200 riverine and hill-dwelling ethnic groups, located principally in the central and southern interior of Borneo, each with its own dialect, customs, laws, territory, and culture, although common distinguishing traits are readily identifiable. Dayak languages are categorised as part of the Austronesian languages. The Dayak were animist in belief; however, since the 19th century there has been mass conversion to Christianity as well as Islam due to the spreading of Abrahamic religions.

South Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. It is the smallest province in Kalimantan, the Indonesian territory of Borneo. The provincial capital was Banjarmasin until 15 February 2022 when it was legally moved to Banjarbaru. The population of South Kalimantan was recorded at just over 3.625 million people at the 2010 Census, and at 4.07 million at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2021 was 4,112,576. One of the five Indonesian provinces in Kalimantan, it is bordered by the Makassar Strait in the east, Central Kalimantan in the west and north, the Java Sea in the south, and East Kalimantan in the north. The province also includes the island of Laut, located off the eastern coast of Kalimantan. The province is divided into 11 regencies and 2 cities. South Kalimantan is the traditional homeland of the Banjar people, although some parts of East Kalimantan and Central Kalimantan are also included in this criteria. Nevertheless, South Kalimantan, especially the former capital city Banjarmasin has always been the cultural capital of Banjarese culture. Many Banjarese have migrated to other parts of Indonesia, as well as neighbouring countries such as Singapore and Malaysia. In addition, other ethnic groups also inhabit the province, such as several groups of the Dayaks, who mostly live in the interior part of the province, as well as the Javanese, who mostly migrated from Java due to the Transmigration program which dated from the Dutch colonial era.

The Malagasy are an Austronesian ethnic group native to the island country of Madagascar.

The Banjar or Banjarese are an indigenous ethnic group native to the Banjar regions in the southeastern Kalimantan hemisphere of Indonesia. Nowadays, Banjarese diaspora can be found in neigbouring Banjar regions as well; including Kotabaru Regency, the southeastern regions of Central Kalimantan, southernmost regions of East Kalimantan, and some provinces of Indonesia in general. The Banjarese diaspora community also can be found in neighbouring countries of Indonesia, such as Brunei, Malaysia, and Singapore.
Barito may refer to:
The East Barito languages are a group of a dozen Dayak (Austronesian) languages of Borneo, Indonesia, and most notably Malagasy, the national language of Madagascar. They are named after the Barito River located in South Kalimantan, Indonesia.
The Barito languages are around twenty Austronesian languages of Indonesia (Borneo), Southern Philippines, plus Malagasy, the national language of Madagascar. They are named after the Barito River located in South Kalimantan, Indonesia.
The Greater North Borneo languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The subgroup covers languages that are spoken throughout much of Borneo, as well as parts of Indonesia, and Mainland Southeast Asia. The Greater North Borneo hypothesis was first proposed by Robert Blust (2010) and further elaborated by Alexander Smith. The evidence presented for this proposal are solely lexical.
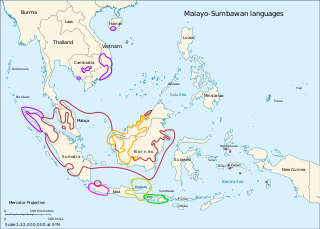
The Malayo-Sumbawan languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian languages that unites the Malayic and Chamic languages with the languages of Java and the western Lesser Sunda Islands, except for Javanese. If valid, it would be the largest demonstrated family of Malayo-Polynesian outside Oceanic. The Malayo-Sumbawan subgroup is however not universally accepted, and is rejected e.g. by Blust (2010) and Smith (2017), who supported the Greater North Borneo and Western Indonesian hypotheses. In a 2019 paper published in Oceanic Linguistics, Adelaar accepted both of these groupings, in addition to Smith's (2018) redefinition of Barito languages as forming a linkage.
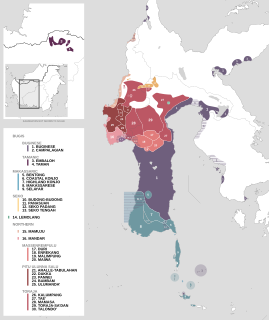
The South Sulawesi languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are primarily spoken in the Indonesian provinces of South Sulawesi and West Sulawesi, with a small outlying pocket in West Kalimantan.

Malagasy is an Austronesian language and the national language of Madagascar. Malagasy is the westernmost Malayo-Polynesian language, brought to Madagascar by the settlement of Austronesian peoples from the Sunda islands around the 5th century AD. The Malagasy language is one of the Barito languages and is most closely related to the Ma'anyan language, still spoken on Borneo to this day. Malagasy also includes numerous Malay and Javanese loanwords, from the time of the early Austronesian settlement and trading between Madagascar and the Sunda Islands. After c. 1000 AD, Malagasy incorporated numerous Bantu and Arabic loanwords, brought over by traders and new settlers.
Bakumpai is an Austronesian language belonging to the West Barito languages. It is spoken by about 100,000 Bakumpai people living in the central Kalimantan, Indonesia.

Ma'anyan, Dayak Maanyan or Eastern Barito Dayak people are a sub-ethnic group of the Dayak people indigenous to Borneo. They are also considered as part of the east Barito Dusun group with the name Dusun Ma'anyan. According to J. Mallinckrodt (1927), the Dusun people group is part of the Ot Danum people cluster, although later that theory was disproved by A. B. Hudson (1967), who argues that the Ma'anyan people are a branch of the Barito family. The Ma'anyan people who are often referred to as Dayak people are also referred to as Dayak Ma'anyan. The Dayak Ma'anyan people inhabit the east side of Central Kalimantan, especially in the East Barito Regency and parts of South Barito Regency which are grouped as Ma'anyan I. The Dayak Ma'anyan people also inhabit the northern parts of South Kalimantan, especially in Tabalong Regency which refers to the Dayak Warukin people. The Dayak Balangan people or Dusun Balangan people which are found in the Balangan Regency and the Dayak Samihim people that are found in the Kotabaru Regency are grouped together with the Dayak Ma'anyan people group. The Dayak Ma'anyan people in South Kalimantan are grouped as Ma'anyan II.
Lawangan or Luangan people are a sub-ethnic of the Dayak Dusun people group, sometimes also referred to as Dusun Lawangan or Dayak Lawangan. The Lawangan people inhabit the eastern side of Central Kalimantan and West Kutai Regency, East Kalimantan, Indonesia. In Tabalong Regency, South Kalimantan, the Lawangan people can be found only in Binjai village. They speak Lawangan language.
Embaloh (Maloh) is an Austronesian (Dayak) language of spoken in West Kalimantan, Indonesia. Apart from Taman, it is not close to other languages on Borneo, but rather belongs to the South Sulawesi languages closest to Buginese. Many speakers of Embaloh also speak Iban, leading to the adoption of some Iban loanwords into Embaloh.
Kendayan, or Salako (Selako), is a Malayic Dayak language of Borneo. The exact number of speakers remains unknown, but is estimated to be around 350,000.
Paku (Bakau) is an Austronesian language spoken in four villages in the East Barito Regency of Central Kalimantan province, Indonesia. It is closely related to the Malagasy language spoken on Madagascar. Most of the remaining speakers are also fluent in other languages. The use of the language is decreasing and speakers are increasingly shifting to Ma'anyan, a lingua franca of East Barito. In 2018, it was estimated there was about 50 speakers of the language in the villages of Tampa, Tarinsing, Bantei Napu, and Kalamus in the regency of East Barito.

Indonesia–Madagascar relations spans for over a millennium, since the ancestors of the people of Madagascar sailed across the Indian Ocean from the Nusantara Archipelago back in 8th or 9th century AD. Indonesia has an embassy in Antananarivo, while Madagascar does not have an accreditation to Indonesia. It was announced in December 2017 that Madagascar would be opening an embassy in Jakarta in 2018, however, as of 2022, Madagascar has not yet opened an embassy in the country.
References
- ↑ Ma'anyan at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Gudai, Darmansyah (1988). A Grammar of Maanyan, A Language of Central Kalimantan. Australian National University.
- ↑ Dahl, Otto Christian (1951). Malgache et maanjan: une comparaison linguistique. Egede-Instituttet Avhandlinger, no. 3 (in French). Oslo: Egede-Instituttet. p. 13.
- ↑ There are also some Sulawesi loanwords, which Adelaar attributes to contact prior to the migration to Madagascar: See Adelaar, K. Alexander (2006). "The Indonesian Migrations to Madagascar: Making Sense of the Multidisciplinary Evidence". In Truman Simanjuntak; Ingrid Harriet Eileen Pojoh; Muhammad Hisyam (eds.). Austronesian Diaspora and the Ethnogeneses of People in Indonesian Archipelago. Jakarta: Indonesian Institute of Sciences. pp. 8–9.
- ↑ Dewar, Robert E.; Wright, Henry T. (1993). "The Culture History of Madagascar". Journal of World Prehistory. 7 (4): 417–466. doi:10.1007/bf00997802. hdl: 2027.42/45256 .
- ↑ Burney, David A.; Burney, Lida Pigott; Godfrey, Laurie R.; Jungers, William L.; Goodman, Steven M.; Wright, Henry T.; Jull, A. J. Timothy (2004). "A Chronology for Late Prehistoric Madagascar". Journal of Human Evolution. 47 (1–2): 25–63. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2004.05.005. PMID 15288523.
- ↑ Kumar, Ann (2012). "Dominion Over Palm and Pine: Early Indonesia's Maritime Reach". In Wade, Geoff (ed.). Anthony Reid and the Study of the Southeast Asian Past. Singapore: Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. pp. 101–122.
- Gudai, Darmansyah H. (1985). A Grammar of Maanyan: A Language of Central Kalimantan (PhD thesis). The Australian National University. doi: 10.25911/5D763957026A1 . hdl: 1885/10904 .